Details
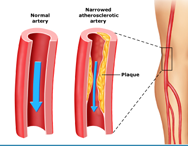
This is the most common type of heart disease and the leading cause of heart attacks. CAD occurs when fat and cholesterol clog the arteries that feed blood to the heart muscle. The clogs prevent blood from flowing smoothly to the heart muscle. Oxygen and nutrients needed for the heart to function are in too short supply, and the heart’s pumping action can be impaired. Sudden formation of a blood clot over the fatty deposit inside the artery can abruptly close the artery, triggering sudden death or heart attack. In addition to taking medications and making lifestyle changes, patients with CAD disease may undergo angioplasty with stent placement or coronary artery bypass surgery.
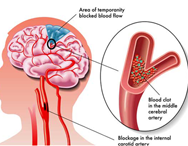
Many people with plaque deposits in the coronary arteries do not have any symptoms, and normal or slightly elevated cholesterol. An ultrasound of the carotid arteries in the neck can reveal narrowing or blockage caused by the accumulation of plaque along the artery walls. Known as a carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) scan, this test is a reliable, noninvasive method to evaluate cardiovascular risk without exposure to radiation. Increased carotid IMT is directly associated with an increased risk for heart attack and stroke.